Free E-book: Developper avec les API Google Maps: Publisher: Dunod | 2010 | ISBN: 2100554034 | French | PDF | 232 pages | Download : Developper avec les API Google Maps
mardi 19 mars 2013
Free E-book: Developper avec les API Google Maps
Free E-book: Developper avec les API Google Maps: Publisher: Dunod | 2010 | ISBN: 2100554034 | French | PDF | 232 pages | Download : Developper avec les API Google Maps
lundi 18 mars 2013
Learn How to Create a Map Topology in ArcGIS 10.1
When editing map data, you often have features that share boundaries. For example, you may have a forest border that meets the edge of a stream or a lake polygon that shares borders with land-cover polygons and shoreline features. Editing with topology can reduce the chance of introducing inadvertent gaps or overlaps between features that share geometry. You can create a simple map topology to make updates simultaneously to all features that are coincident.
Aligning features and editing coincident geometry through topology has been made easier with ArcGIS 10.1. The new Select Topology dialog box consolidates into one step the process of creating and activating a map topology, which is available for all license levels of ArcGIS for Desktop.
To create a map topology in ArcMap, first add all the layers you want to edit together to your map. You can edit geodatabase feature classes or shapefiles with a map topology.
Step one: Click Customize, point to Toolbars, and add the Editor and Topology toolbars to ArcMap. The Topology toolbar has been redesigned in ArcGIS 10.1 so that it contains only commands that are directly related to topology. All other commands previously on this toolbar, such as Construct Polygons, have been moved to the Advanced Editing toolbar.
Step two: On the Editor toolbar, click the Editor menu and click Start Editing to begin an edit session.
Step three: On the Topology toolbar, click Select Topology. This opens the Select Topology dialog box.
Step four: Check the layers that should be edited together. In ArcGIS 10.1, map topology uses layer information and reflects layer properties, including name and visibility, rather than the properties of the underlying feature class as it did in previous releases. Annotation, dimension, or feature classes that participate in a geometric network cannot be included in a map topology.
Step five: Optionally, click Options to view the cluster tolerance, which is the distance that defines how close together edges and vertices must be to be considered coincident. Because ArcMap automatically determines the minimum possible cluster tolerance, you should generally use the default, because increasing the value can cause features to collapse or distort. To get information about what you can do with topology, click the About editing topology link. This opens the related topic in the help system.
Step six: Click OK.
That's all you need to do to set up a map to edit coincident features. If you happened to click a topology editing tool without already having a topology set up, you would be prompted to create a map topology using this dialog box.
Now that you have an active topology, edit with the tools on the Topology toolbar to make sure your features remain coincident. Use the Topology Edit tool to select edges so that you can move, modify, and reshape them. If you want to select multiple edges that form a path so you can reshape them all at the same time, you can either use the new Topology Edit Trace tool or simply hold down the left mouse button using the Topology Edit tool.
To learn more about enhancements to editing features with topology, see the Editing topology and New tools for aligning data sections in "What's new for editing in ArcGIS 10.1."
thanks to
By Rhonda Glennon
ArcGIS Product Engineer
samedi 2 mars 2013
How to connect spatial database(PostGIS) with QGIS?
In this section, I am showing the 3 basic steps to connect PostGIS database with a widely used open source desktop based gis, QGIS.
Step1: Install PostGIS with Spatial database support extension
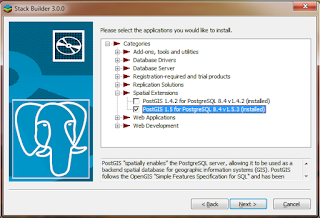
- If PostgreSQL is already installed è Launch ‘Application stack builder’ from startup menu in windows 7.
- Select the appropriate instance of PGSQL from dropdown list and Click NEXT.
- Expand ‘Categories’è Expand ‘Spatial Extensions’ è Select appropriate PostGIS version(1.5) for the already installed PGSQL version(8.4).
- Follow the instructions to install the PostGIS extension.
Step2: Loading spatial data into PostGIS
- Open the PgAdmin window (above installation should install a ‘Shapefile to PostGIS importer’ plugin.)
- Select the database and click on ‘Plugins’ and select ‘Shapefiel to PostGIS importer’ plugin.
- If the plugin is not available under the ‘Plugins’. We can also get it from “C:\Program Files (x86)\PostgreSQL\8.4\bin\postgisgui\shp2pgsql-gui.exe”
- Select the desired shp file to put into PostGIS.
- We need to put the appropriate SRID for the imported file. SRID column contains datum information of the imported shapefile into the PostGIS. There are unique SRID for the different projection and datum types.
- Above step feeds the spatial information into the database with two additional fields, one for vector geometry id and another for vector geometry with datum information.
Step3: Retrieving spatial data from PostGIS into Web based applications and Desktop based applications.
- We can view and project above data using Qgis(An open source GIS alternative to ESRI’s ArcGIS) in desktop based environment. Similarly, we can use Geoserver or UMN Mapserver view data in the Web.
- The core technologies behind Qgis and GRASS are similar. Qgis is easy to use, support GDAL, Python, PostGIS, and has nice GUI. In the same time we can get strength of GRASS by calling GRASS’s functionality form the QGIS.
- Install Qgis
- Open the Qgis --> Click layer--> select ‘Add from PostGIS’, which gives you the following windows.
Inscription à :
Commentaires (Atom)



